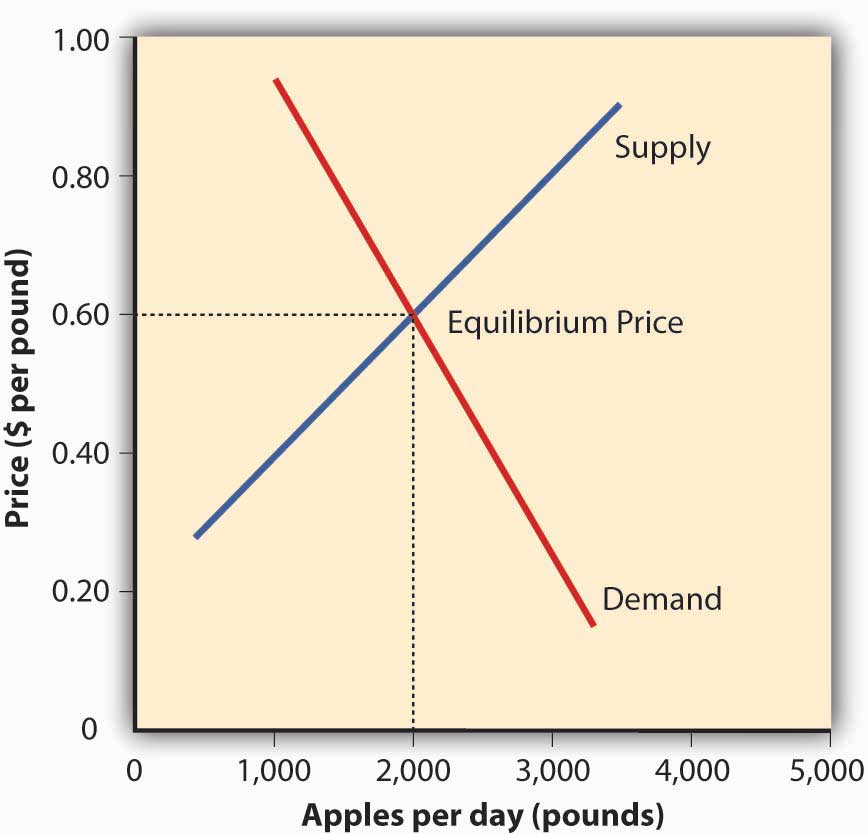
Cost Function Equilibrium . i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. equilibrium with different cost functions. topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. P = 50 − 2q and c =. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; Let the inverse demand function and the cost function be given by. when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,.
from saylordotorg.github.io
Let the inverse demand function and the cost function be given by. P = 50 − 2q and c =. when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. equilibrium with different cost functions. each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y;
Perfect Competition and Supply and Demand
Cost Function Equilibrium i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. Let the inverse demand function and the cost function be given by. topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. P = 50 − 2q and c =. each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. equilibrium with different cost functions.
From saylordotorg.github.io
The ISLM Model Cost Function Equilibrium P = 50 − 2q and c =. i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. The inverse demand function for the. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Oligopoly PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID809915 Cost Function Equilibrium P = 50 − 2q and c =. each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. The inverse demand. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From demonstrations.wolfram.com
Cournot Competition with Two Firms Wolfram Demonstrations Project Cost Function Equilibrium when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p =. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.researchgate.net
Equilibrium for a smoothed marginal cost function, for a = 14, b = c Cost Function Equilibrium i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. P = 50 − 2q and c =. each of two firms has. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.youtube.com
Finding Longrun Equilibrium from Cost FunctionsII YouTube Cost Function Equilibrium when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. equilibrium with different cost functions. Let the inverse demand function and the cost function be given by. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. topics include how to. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Equilibrium Introduction to Business Cost Function Equilibrium equilibrium with different cost functions. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. i am having a lot of problems trying. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From analystprep.com
Longrun Equilibrium Under Each Market Structure AnalystPrep CFA Cost Function Equilibrium P = 50 − 2q and c =. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. topics include how to use a market model to. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Equilibrium, Price, and Quantity Introduction to Business Cost Function Equilibrium each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; P = 50 − 2q and c =. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.tutor2u.net
Perfect Competition Short Run Price and Output… tutor2u Economics Cost Function Equilibrium Let the inverse demand function and the cost function be given by. topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. We have. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.mrbanks.co.uk
Price Mechanism — Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources, Tutoring & Exam Prep Cost Function Equilibrium Let the inverse demand function and the cost function be given by. P = 50 − 2q and c =. topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. equilibrium with. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.solutionspile.com
[Solved] 2. Find the equilibrium values of and int Cost Function Equilibrium i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. topics include how. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.chegg.com
Solved An economist estimated that the cost function of a Cost Function Equilibrium each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. i am having a lot. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Relative Profit Maximization and Bertrand Equilibrium with Convex Cost Function Equilibrium each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have the same. when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. i am having a lot of problems trying to find. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.youtube.com
Finding the Longrun Equilibrium from Cost FunctionsI YouTube Cost Function Equilibrium equilibrium with different cost functions. i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. Let the inverse demand function and the cost function be given by. The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output.. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.youtube.com
Ex Given the Cost and Demand Functions, Maximize Profit YouTube Cost Function Equilibrium The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. P = 50 − 2q and c =. topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity change in a market when demand changes, supply. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From study.com
Applying Systems of Linear Equations to Market Equilibrium Steps Cost Function Equilibrium The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. equilibrium with different cost functions. We have discussed equilibrium when all firms, both potential and actual, have. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.youtube.com
Given Demand and Cost Functions Find level of output and price that Cost Function Equilibrium Let the inverse demand function and the cost function be given by. each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; P = 50 − 2q and c =. i am having a lot of problems trying to find the equilibrium price when we are given a cost function and demand. equilibrium with different cost. Cost Function Equilibrium.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The economy is in the shortrun macroeconomic Cost Function Equilibrium The inverse demand function for the firms' output is p = 120 q, where q is the total output. P = 50 − 2q and c =. equilibrium with different cost functions. each of two firms has the cost function tc(y) = 30y; topics include how to use a market model to predict how price and quantity. Cost Function Equilibrium.